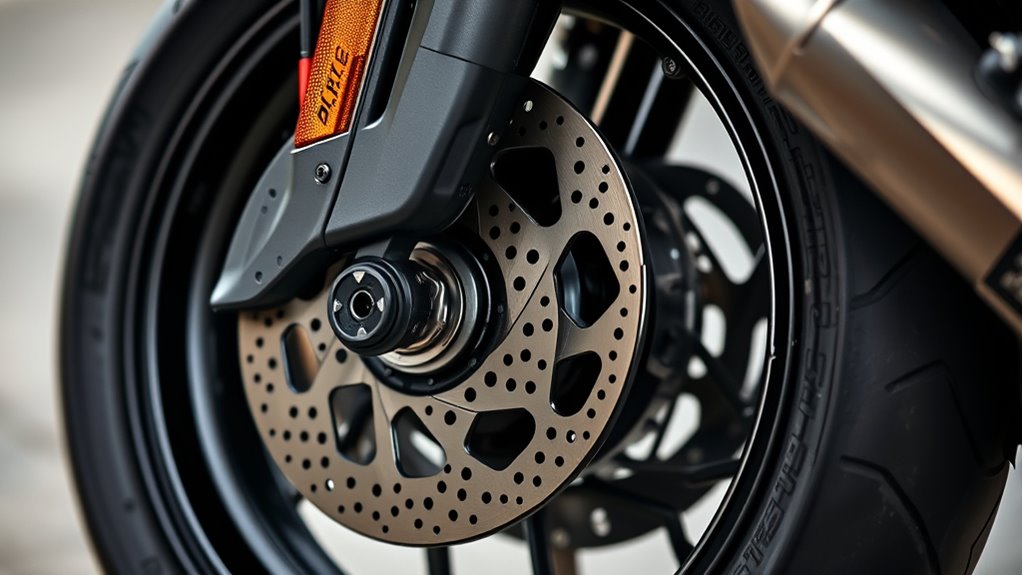
Beta: Rear brake force distribution is essential for keeping your vehicle stable and ensuring safe stopping. It involves adjusting how much braking power goes to the rear wheels, which helps prevent lockup or fishtailing. Proper balance improves safety and reduces stopping distance, especially in different driving conditions. By understanding how pressure modulation works, you can optimize your braking performance. Keep exploring to uncover how these adjustments can make your braking smoother and more reliable.
Key Takeaways
- Proper rear brake force distribution prevents rear wheel lockup and maintains vehicle stability during braking.
- Modern systems use sensors and electronic control to dynamically adjust brake pressure to the rear wheels.
- Adjusting rear brake force influences stopping distance, safety, and overall vehicle handling.
- Brake force balance is typically weighted toward the front wheels due to weight transfer during deceleration.
- Regular maintenance and calibration of brake modulation systems ensure optimal rear brake force distribution.
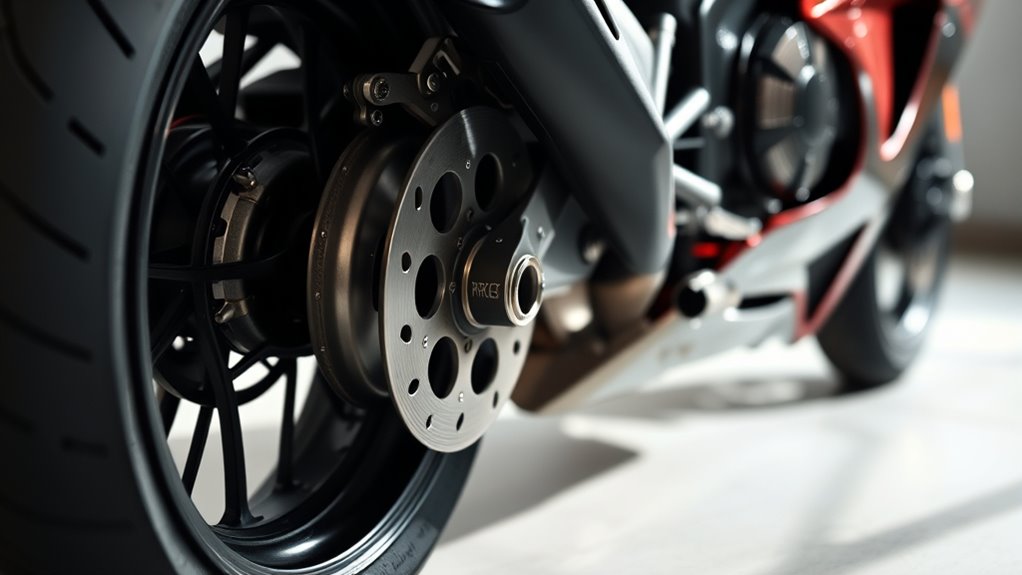

Understanding rear brake force distribution is essential for enhancing your vehicle’s braking performance and safety. When you apply the brakes, the way the braking force is split between the front and rear wheels directly impacts your control and stopping distance. Proper braking balance ensures that neither set of tires is overloaded, which can lead to skidding or loss of control. Achieving an ideal balance involves adjusting how pressure modulation occurs within your braking system, so you can respond effectively to different driving conditions.
Proper brake force balance ensures vehicle control and safety during stops.
Your vehicle’s braking system is designed to distribute force based on the dynamics of your ride. Typically, more braking force is sent to the front wheels because they handle most of the vehicle’s weight transfer during deceleration. However, if too much force goes to the rear, you risk rear-wheel lockup, which can cause fishtailing or a loss of directional control. Conversely, if too little force reaches the rear, your stopping distance might increase unnecessarily, compromising safety. The key is to fine-tune braking balance through pressure modulation, which allows you to control how much brake pressure each wheel receives, especially during sudden or intense braking.
Pressure modulation plays a critical role because it enables you to adjust brake force dynamically. Modern brake systems, especially those with electronic stability control and ABS, automatically modulate pressure to optimize braking balance. As you brake, sensors monitor wheel speed and vehicle stability, adjusting brake pressure in real time to prevent lockup and maintain control. In manual systems, you can influence pressure modulation through brake pedal feel and technique, applying steady pressure to distribute force evenly. Many high-performance vehicles feature adjustable brake bias, giving you the option to customize the front-to-rear force distribution based on driving conditions or personal preference. Additionally, understanding the role of pressure modulation helps in diagnosing and maintaining your braking system for peak performance.
Getting a good handle on how pressure modulation affects braking balance can dramatically improve your safety. When you understand how to manage and anticipate changes in brake force distribution, you’ll be able to brake more confidently on slippery roads, during emergency stops, or when carrying heavy loads. Properly calibrated braking systems allow for smoother deceleration, reducing wear on brake components and enhancing overall vehicle control. By paying attention to how your brakes respond and making adjustments where applicable, you can optimize the rear brake force distribution, ensuring that your vehicle responds predictably and safely under all conditions.
In essence, mastering braking balance and pressure modulation empowers you to brake more effectively, improving safety and performance every time you step on the pedal.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Beta Adjust Rear Brake Force During Cornering?
During cornering, Beta adjusts rear brake force by fine-tuning brake modulation to optimize handling dynamics. You’ll notice that the system reduces rear brake pressure when you lean into a turn, preventing rear-wheel lock-up and enhancing stability. This active adjustment helps you maintain control, improves cornering confidence, and guarantees smoother transitions through curves, allowing you to focus on your riding line without worrying about rear end instability.
Can Rear Brake Force Distribution Be Customized for Different Riding Styles?
Yes, you can customize rear brake force distribution to suit your riding style. With adjustable options, you control brake balance, blending braking power between the rear and front wheels. This personalization allows for precise, perfect control, whether you prefer aggressive, agile, or smooth, steady stops. By tweaking these customization options, you guarantee your ride responds exactly how you want, making every maneuver more manageable and tailored to your technique.
What Impact Does Rear Brake Force Have on Overall Bike Stability?
Rear brake force directly affects your bike’s stability by influencing brake balance and stability control. Too much rear brake can cause instability, especially during aggressive turns or sudden stops, while too little might reduce braking efficiency. Proper rear brake force enhances overall stability by maintaining balanced brake feedback, allowing you to control the bike confidently. Adjusting brake force ensures reliable brake balance, helping you stay stable and in control in various riding conditions.
How Does Rear Brake Force Distribution Affect Tire Wear?
You’ll notice that rear brake force distribution directly impacts tire wear by influencing brake balance. Applying too much rear brake can cause uneven tire wear, reducing tire longevity over time. Conversely, balanced brake force helps distribute braking forces evenly, preserving tire life. Proper brake balance ensures you maximize tire longevity and maintain ideal grip, preventing premature wear and enhancing overall riding performance.
Is Rear Brake Force Distribution Different for Off-Road Versus On-Road Riding?
You might think rear brake force distribution is the same for off-road and on-road riding, but it actually varies to match conditions. Off-road riding requires more delicate brake modulation and braking techniques to prevent slipping on loose surfaces, so rear brake force is often reduced. On-road, you can apply more rear brake for stability, using firmer brake modulation. Adjusting rear brake distribution enhances safety and control in different riding environments.
Conclusion
By balancing brake force between the rear and front, you boost bike balance and brink bike blunders. Proper rear brake force distribution delivers deliberate, dependable deceleration, decreasing danger and diminishing drifts. Don’t disregard the delicate dance of distribution — discipline and detail drive your riding’s durability. Devote time to dialing your rear brake force, and you’ll discover a safer, smoother, more synchronized cycling experience. Remember, mastering meticulous modulation makes your motorcycle mastery truly magnificent.